Non-woven fabrics are a fascinating category of materials that have gained significant popularity in various industries. Unlike traditional woven fabrics that are constructed by interlacing yarns, non-woven fabrics are manufactured by bonding or interlocking fibers together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes. This unique composition imparts several advantageous properties to non woven fabrics, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. In this article, we will explore different examples of non-woven fabrics and delve into their diverse uses across various sectors.
Introduction
Non-woven fabrics have revolutionized numerous industries due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and superior performance characteristics. These fabrics are created by directly bonding or felting fibers together, eliminating the need for weaving or knitting processes. With their exceptional properties and diverse range of applications, nonwoven fabrics have become an indispensable part of our everyday lives.
Non-woven Fabric Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of non-woven fabrics involves several techniques, each contributing to the unique characteristics of the final product. The most commonly used methods include spunbonding, meltblowing, needle-punching, and wet-laid processes. Each technique entails specific steps that result in distinct nonwoven fabric types.
Types of Non-woven Fabrics
1. Spunbond Non-woven Fabrics
Spunbond nonwoven fabrics are manufactured by extruding continuous filaments of thermoplastic polymers, such as polypropylene or polyester.
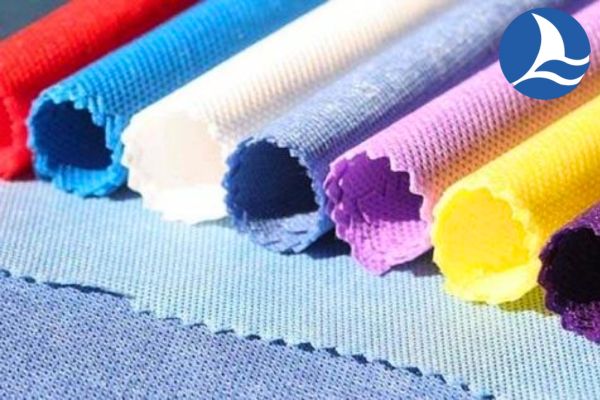

These filaments are then laid down onto a conveyor belt, forming a web. The web is subsequently bonded through heat or chemical processes, resulting in a durable and uniform nonwoven fabric.
2. Meltblown Non-woven Fabrics
Meltblown nonwoven fabrics are produced using a meltblowing technique, where high-velocity hot air is used to attenuate molten thermoplastic polymers into microfibers.
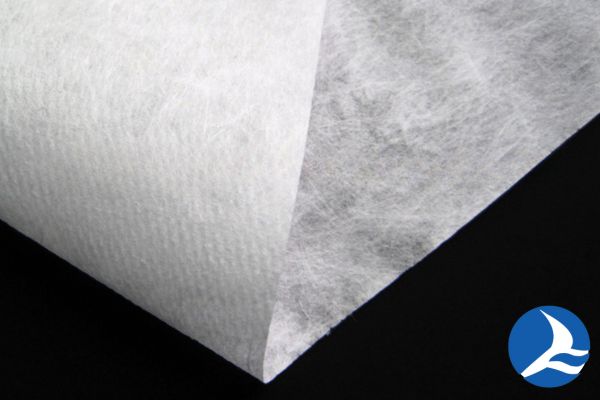
The microfibers are collected and randomly deposited to form a web. Meltblown fabrics exhibit excellent filtration properties and are commonly used in medical masks, air filters, and oil sorbents.
3. Needle-punched Non-woven Fabrics
Needle-punched nonwoven fabrics are created by mechanically entangling fibers using barbed needles. This process enables the fibers to interlock, resulting in a fabric with enhanced strength and dimensional stability.
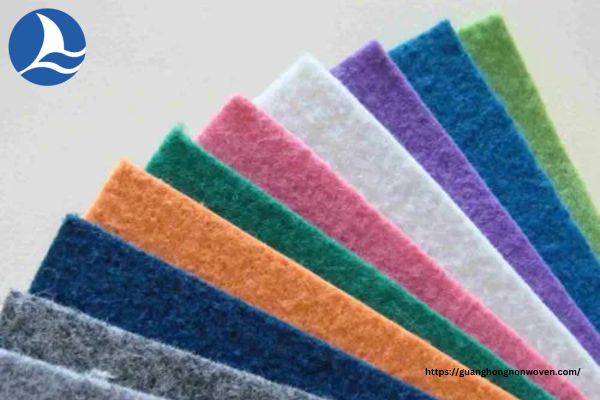

Needle-punched fabrics find applications in automotive interiors, carpets, upholstery, and geotextiles.
4. Wet-laid Non-woven Fabrics
Wet-laid nonwoven fabrics are manufactured by suspending fibers in a liquid solution and depositing them onto a forming screen. The fibers are then bonded together using mechanical or chemical methods.

Wet-laid fabrics possess excellent absorbency and are often used in medical wipes, tea bags, and filtration media.
Applications of Non woven Fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics find extensive applications across a wide range of industries due to their exceptional properties and versatility.

1. Medical and Healthcare
In the medical and healthcare sector, non-woven fabrics are utilized in surgical gowns, drapes, disposable bed sheets, face masks, and wound dressings. These fabrics provide a barrier against microorganisms, are breathable, and offer excellent comfort.
2. Geotextiles and Construction
Non-woven geotextiles play a crucial role in erosion control, drainage systems, road construction, and landscaping. These fabrics provide stabilization, filtration, and separation functions, enhancing the durability and performance of civil engineering projects.
3. Automotive
Automotive applications of non-woven fabrics include carpeting, upholstery, headliners, trunk liners, and engine components. Nonwoven fabrics offer noise insulation, thermal resistance, and improved aesthetics in the automotive industry.
4. Filtration
Nonwoven fabrics are widely used in air and liquid filtration systems. They effectively capture particles, contaminants, and pollutants, making them suitable for applications such as HVAC filters, water purification, and industrial filtration.
5. Personal Care and Hygiene Products
Nonwoven fabrics are extensively used in personal care and hygiene products, including baby diapers, feminine hygiene products, wet wipes, and adult incontinence products. These fabrics provide softness, liquid absorption, and comfort to the users.
6. Packaging
Nonwoven fabrics find applications in packaging industries, particularly for making reusable shopping bags, gift wraps, and promotional bags. These fabrics offer durability, eco-friendliness, and customization options.
7. Agriculture
In agriculture, nonwoven fabrics are employed as crop covers, mulch mats, nursery pots, and greenhouse shading. These fabrics enhance crop growth, protect against pests and harsh weather conditions, and provide effective weed control.
8. Furniture and Bedding
Nonwoven fabrics are used in furniture and bedding applications, such as mattress covers, upholstery, and pillow protectors. These fabrics offer breathability, moisture resistance, and durability to enhance the comfort and longevity of furniture and bedding products.
9. Apparel and Fashion
Nonwoven fabrics are increasingly finding their way into the fashion industry. They are used for garment interlinings, shoe linings, and accessories. These fabrics provide structure, lightweight comfort, and unique design possibilities.
10. Environmental Protection
Nonwoven fabrics contribute to environmental protection through applications like oil spill cleanup materials, sediment control barriers, and eco-friendly packaging alternatives. These fabrics play a crucial role in sustainability and waste reduction efforts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Non-woven Fabrics
Non-woven fabrics offer several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, breathability, versatility, and ease of manufacturing. However, they also have some limitations, such as lower tensile strength compared to woven fabrics and limited recyclability. Understanding the pros and cons of nonwoven fabrics helps in selecting the appropriate material for specific applications.
Conclusion
Non-woven fabrics have revolutionized industries with their versatility, performance, and wide-ranging applications. From medical and healthcare to automotive and environmental protection, these fabrics offer unique properties that cater to diverse needs. Their cost-effectiveness, ease of manufacturing, and advantageous characteristics make them a preferred choice in various sectors.
FAQs
Are non-woven fabrics environmentally friendly?
Yes, nonwoven fabrics can be environmentally friendly, especially when they are made from recycled materials or have recyclability features.
Can non-woven fabrics be washed and reused?
Some nonwoven fabrics can be washed and reused, depending on their composition and intended use. However, not all non-woven fabrics are designed for multiple uses.
Are non-woven fabrics suitable for sensitive skin?
Yes, nonwoven fabrics are often used in personal care products and medical applications because they are hypoallergenic and gentle on the skin.
Can non-woven fabrics withstand high temperatures?
The thermal resistance of nonwoven fabrics varies depending on their composition. Some non-woven fabrics can withstand high temperatures, while others may have limitations.
Are non-woven fabrics biodegradable?
Not all nonwoven fabrics are biodegradable. However, there are biodegradable options available in the market, which contribute to sustainable practices.
