Non-woven fabrics have gained a lot of traction recently, resulting in non-woven fabric manufacturers getting packed with orders and forced to increase production. This is good news for the industry and even the consumers; with increased demand, the competition will increase, resulting in lowered prices and improved quality of the non-woven fabric.

But it is not just about getting the goods from any non-woven fabric supplier; rather, consumers should always look for the best non-woven fabric manufacturers and should conduct research on top quality non-woven fabric factories before placing an order. In this article, we will briefly introduce non-woven fabric and cover all relevant aspects that a consumer must be aware of before placing an order with any non-woven fabric manufacturer or supplier.
What is Non-woven fabric?
Non-woven fabric is natural, but contrary to traditional woven fabrics, it doesn’t have any interwoven strands. However, it does have an organized internal structure. It is primarily made from staple and long fiber that either has bonded:
- Chemical treatment
- Mechanical treatment
- List Item #3
- List Item
These above-mentioned treatments turn the fibre into a cohesive fiber-like material. Although the fabric lacks the traditional strength of fabric, it can be fortified by reinforcing it with a backing, or it can be made dense to add strength to it. In recent times, it has become an excellent alternative to polyurethane foam.
Non-woven fabric requires no knitting or weaving. Felt, which is one of the most common types of non-woven fabric, is made by treating fiber in chemical solvent until the fiber forms an interlocked textile that is dense.
Manufacturing Process:
The manufacturing process for non-woven fabric is a series of steps that determine the characteristics and properties of the fibre produced. It is then categorized and filtered as per the desired application.

The steps include web formation of the fibres to produce structural integrity to display characteristics that the fibre was specifically crafted for finally. The steps are discussed in detail below:
1. Web Formation:
Web formation plays an important part in determining the characteristics of the fabric to be produced. The length and strength of the fabric play a key role in determining the method for web formation. Although several techniques for web formation are currently deployed, for staple fibres, the techniques are based on the textile carding process. For short fibres, it is based on a process that is similar to paper manufacturing called the wet-laid process. Some techniques have been developed that form web directly from filaments that come from spun laid extruders.
The fabric produced is not strong in nature, which is then subjected to further treatment to develop properties that make it useful.
2. Web Bonding
We briefly mentioned some treatments that are used for the manufacturing of non-woven fiber. They are primarily used during the web bonding phase, which follows web formation. The most common web bonding techniques include:
Stitch Bonding:In this method, fiber webs are consolidated using knitting elements, either with or without yarn, that help to interlock the fiber with the freedom to use a variety of yarns. Stitch bond fabric is taking the place of woven fabric in a number of applications as it is easier and quicker to manufacture. This automatically lowers the cost of production. The applications for this type of fabric include its use as interlining, for filtration, for vacuum bags and even geotextiles.
Needle Punching:It is a mechanical method to bond non-woven web structures. Non-aligned barbed needles are used in this process. They are mounted on a board and used for punching the fiber through the web. When it gets withdrawn, the fiber gets entangled, and the needle board gets easily withdrawn thanks to the needles being unaligned.
Chemical Bonding: As the name suggests, chemical bonding agents are used for manufacturing fibre this way and it is one of the most popular methods in the non-woven industry. the process involves applying the chemical binder and curing the fabric later. There are several methods for application of bonder this way, including spraying, printing, foaming, and saturation bonding. Latex is a commonly used binding agent as it is both, cheap and easy to use.
Water Entanglement or Hydro Entanglement: The process involves using pressure exerted by liquids that bond the fiber to form the fabric. High-pressure water jets are used to direct the water through the web. This creates entanglement when the web is struck by high-pressure water jet and it deflects the fibers.
Heat based or Thermal Bonding: Heat is utilized for the stabilization of fibre-based thermoplastic in this process. Since the entire fiber acts as a binder, this process doesn’t require any chemical binders to hold the fibers together. It is a popular method for manufacturing baby diapers by the cover stock industry. The most suitable and common type of fiber used in this process is polypropylene. It has a low melting point and it is soft and comfortable.
Applications of Non-Woven Fabric:
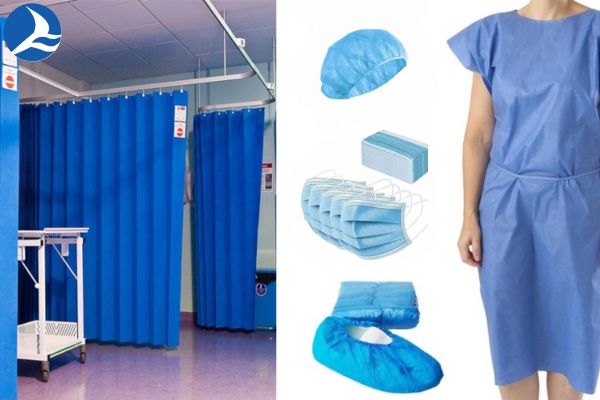
Non-woven fabric has versatile applications and serves many industries ranging from medical, filter, geo-textile and many others. Some popular medical applications are listed below:
- For medical applications, they are used to manufacture isolation gowns; surgical gowns, covers, and drapers; surgical masks, caps, scrubs, suits, gloves, and shoe covers.
- They are also used to produce high-quality bath wipes, wound dressings, and plasters.
- They are also used for drug delivery to manufacture isolation covers for sensitive drugs.
In light of the recent COVID-19 pandemic, non-woven fabric is highly in demand for the manufacturing of facial masks. They are similar to medical-grade face masks or surgical face masks. The most popular among them is the N95 face mask. It is also being used for the manufacturing of Coronavirus safety products. Ensure your Coronavirus safety wear is made of high-quality non-woven fabric only.
