Spunbond Fabric Manufacturing Process
Spunbond nonwoven fabric is one of the most popular non-woven materials. Spun bonding is one of the most common ways to make polymer-laid spunbond nonwovens. The melt spinning technique is used in this process. Spin pumps drive the melt through a spinneret with a large number of holes. The conditioned air is continuously supplied to the filaments through the quench air ducts positioned beneath the spinneret block. A continuous source of auxiliary room temperature is also available.
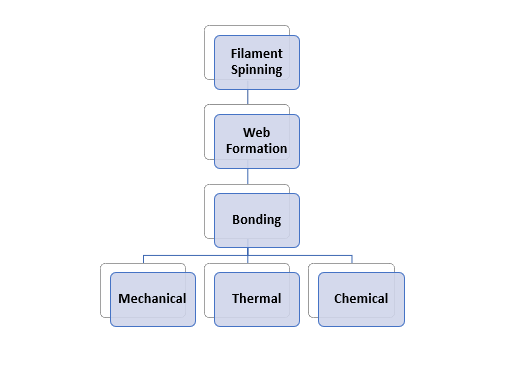
The nonwoven fabric of the spun-bond type is processed as follows:
Filament Spinning

A ventilator-generated under-pressure sucks the filaments and mixed air down from the spinnerets and cooling chambers in the entire working width. Over the line’s whole working length, there is a venture (high-velocity low-pressure zone) to a distributing section that affects fanning and entanglement. Finally, the filaments are deposited on a moving sieve belt as a random web. The turbulence in the airstream causes randomness; however, there is a minor bias in the machine direction due to the moving belt’s directionality. The part below the sieve belt helps the filaments lay down better.

Web Formation
The filament bundles are pneumatically deposited onto a moving belt, forming the web. The fiber formation determines the fabric’s weight to belt speed ratio. Individual filaments must be separated before reaching the belt for the web to attain optimal uniformity and coverage. This is achieved by using an electric charge, mechanical or aerodynamic forces to separate the particles.
Bonding
In this technique, any available bonding approach, such as chemicals, mechanical, or thermal, can be employed to produce bonding.
1. Thermal Bonding
The most general approach is thermal point bonding, which uses temperature and pressure to achieve fiber-to-fiber fusion. The surface temperature of the calendar rolls must be selected suitably to obtain good characteristics with the retention of optimum hand/feel in the final fabric. With increasing bonding temperature, both strength, and elongation increase, dropping after reaching an excellent value.
2. Chemical Bonding
This fabric is made using starch or any glue as a chemical. So the bonding of the adhesive with the yarn must be strong.
3. Mechanical Bonding
Mechanically bonding means how much tension or tension the yarn is being twisted with adhesive and its durability, stability.
Application of Spunbond Nonwoven

Spun bond polypropylene has a wide range of applications, including:
- Medical grade nonwoven products
- Bed bases and mattress covers
- Cushion linings
- Tablecloths that can be thrown away
- Work clothes that can be thrown away
- Sanitary products
Spunbond Nonwoven Drawback
The spun bond nonwoven fabric has several drawbacks like:
- Inadequate strength
- Failure to last
- It cannot be cleaned in the same way as other fabrics.
- The fibers are placed in a specific orientation, making it simple to split at right angles and different angles.
